What Is Product Design

In a nutshell, product design encompasses the process of creating a product, from understanding the problem to creating a solution.
Product design really is the unsung hero of the product world. No one notices if you do it really well, but everyone notices if you don’t! Instinctively, we all know what bad design looks like. Which means your customers know what bad design looks like.
Even if you’re not a Product Designer, knowing more about good product design will make you a better Product Manager.
Here we’ll go over the history of Product Design, the fundamental elements of good UX, and a who’s who of the design team.
A Brief History of Product Design
Product design used to be relegated to the world of physical products. It started out as ‘industrial design’ which was the commonly used term before mass-production became the most common way to get products to market.
Now, we can use it to describe both hardware and software design.
The person who created the device you’re reading this on? A product designer.
Whoever created your favorite video streaming app? A product designer.
The team who made your email inbox interface? Product designers…you get the idea.
While no company has ever gone out of their way to build ugly products, when consumer tech really started taking off in the late-eighties/mid-nineties, what mattered most was that the technology worked. Who cares if it only comes in beige? Saying that the nineties was an era that produced notable events that would shape the world for generations to come. And that includes the product world.

Apple’s Product Design Revolution
Google’s Director of UX, Abigail Hart Gray, points to the iMac as an example of a big company first discovering the importance of aesthetics.
As Abigail says, “not having design thinking involved early on meant the engineer would hand over to the designer and essentially say, ‘pretty it up’ with no room for them to ask questions and recommend changes.”
When the first Macintosh came out in the 70s, it wasn’t the prettiest thing ever. It came only in that specific shade of sandy grey with chunky brown plastic keys. People loved working on their Macintosh, but they didn’t particularly love looking at it.
When the iMac G3 came out in 1998, in the shade dubbed Bondi-blue after the waters at Bondi beach, people fell in love. Then-VP of Industrial Design, Jony Ive, asked himself “What computer would The Jetsons have had?” As the first computer Apple was designing for the internet era, I’ve wanted ‘the future’ to be reflected in the design.

So Apple took a retro-futuristic design inspired by the tech of The Jetsons, vintage computer terminals, and the bright colors of 1960’s Olivetti typewriters. What they came up with certainly stood out in a market full of corporate beige.
From there, product experts have been striving for the best product design, bringing together a number of criteria and components. With so many of the same products in the marketplace (hundreds of smartphones, fitness trackers, streaming services, etc) good product design is the key to standing out.
The UX Honeycomb
Product design professionals generally regard The UX Honeycomb by Peter Morville as the classic diagram for the seven essential aspects of UX. It has certainly been argued over, but for beginners, it’s a great introduction to the best product design components.
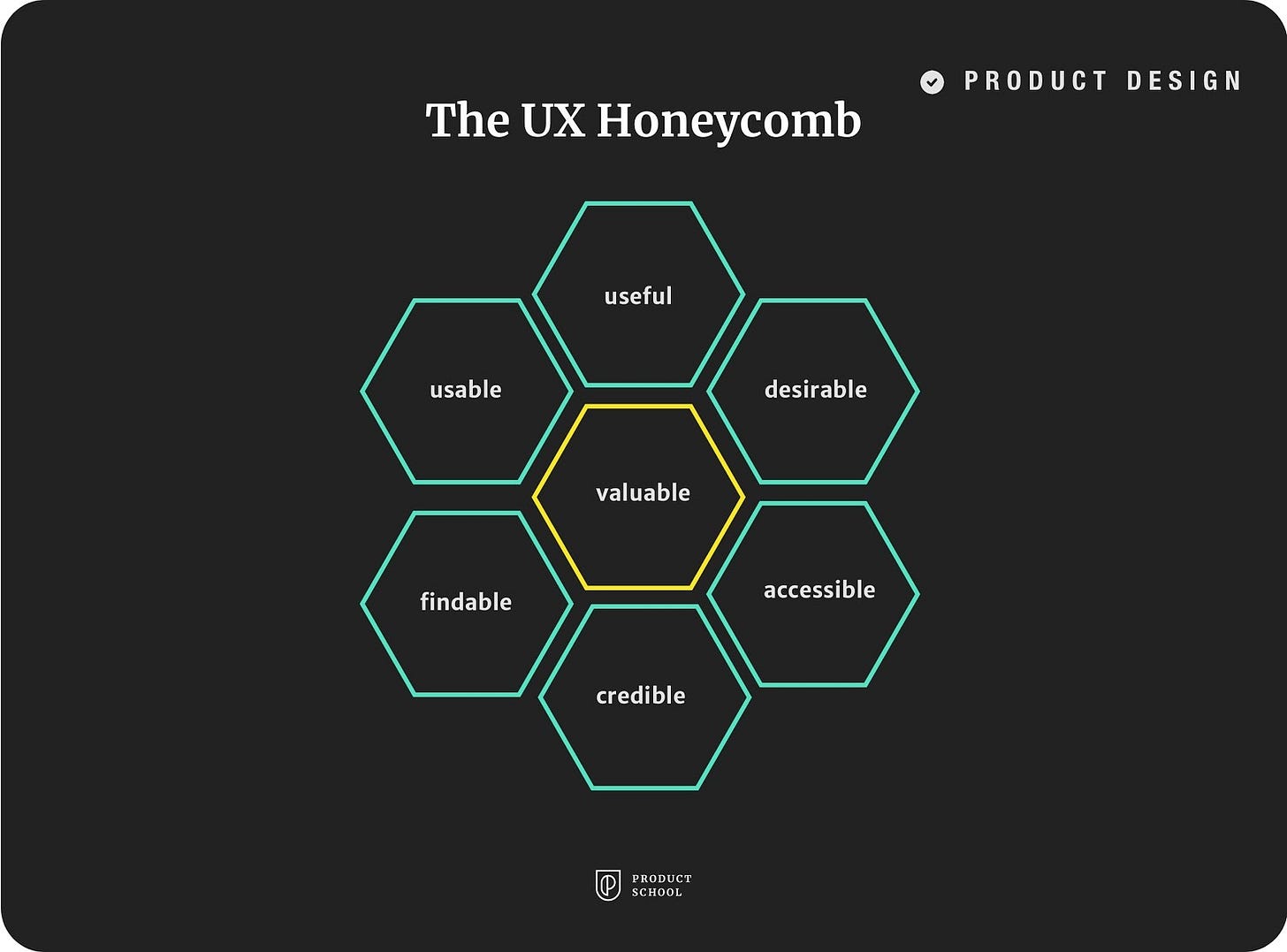
Useful: A product that fills a need, solves a problem, or serves a purpose. It doesn’t have to be useful for every person on the planet, but it needs to serve a target audience.
Usable: Similar, but not the same as useful. Usable reflects how easy it is to navigate your product. If your product takes half an hour to solve a ten-minute problem, it is not usable.
Findable: This focuses on the information architecture of your product. A new user needs to be able to find what they want with relative ease. Findable products have intuitive navigational structures.
Credible: Particularly important in today’s privacy-obsessed world. You need to build a product that deserves the trust of your customers. Avoiding dark patterns and only partnering with trustworthy third-parties is a good start.
Accessible: Around 19% of Americans use accessibility tools to surf the web. A good Product Manager is also a good person and wants their products to be available to whoever needs them. Accessibility is also a legal requirement in many countries.
Desirable: Branding and storytelling will play a big part here, but it’s also about the overall quality of your product.
Valuable: The best product design doesn’t just check all of these boxes. Your product still needs a USP, something which goes the extra mile, delights customers, and slays the competition.
Good Product Design vs Bad Product Design
Bad Product Design: Chasing Products
Your product might not be that bad. In fact, it might actually be pretty good. But if you’ve designed it just to match what a competitor is doing, I’ve got some bad news. You’ve made a chasing product.
When Steve Jobs first unveiled the iPod, all of Seattle could practically hear the teams at Microsoft rushing to catch up. Raise your hand if you own a Zune…
The former leader of Microsoft’s home entertainment and mobile business, Robbie Bach, spoke to Business Insider in 2012 about why the Zune flopped.
What it all came down to was who got to market first.
“The portable music market is gone and it was already leaving when we started. We just weren’t brave enough, honestly, and we ended up chasing Apple with a product that actually wasn’t a bad product, but it was still a chasing product, and there wasn’t a reason for somebody to say, oh, I have to go out and get that thing.”
-Robbie Bach
Before you say that Zune didn’t have a USP compared to the iPod, it actually did. In 2006, Zune’s ability to wirelessly send a song from one device to another was way ahead of its time. But unfortunately, Apple’s incomparable storytelling ability had won over the market.
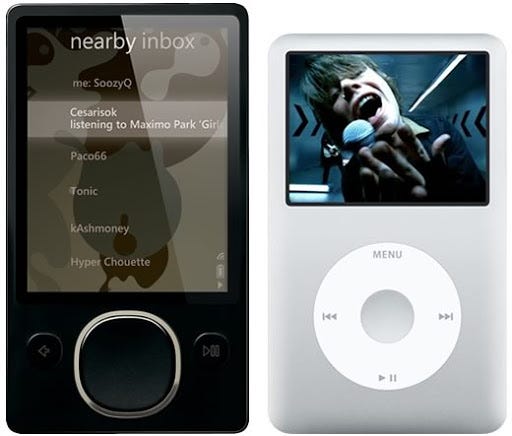
When thinking about your product design, try to avoid creating something that only exists to compete with another company. Unless you have a genuine reason to believe you can do it better! Strive to create something that’s authentically yours.
Good Product Design: ClassPass’ Feedback Modals
Sometimes it’s not just about what good product design can do for your users, it’s what good product design can do for you.
By collecting user feedback at the right times, and gathering the right insights, you can offer the appropriate recommendations for your users. ClassPass does this very well by asking for feedback from users on the level of the class.
By understanding how their users rank different classes in terms of difficulty, they avoid sending their beginner users to “beginner” classes which are actually quite intense. That’s enough to put a customer off forever!

ClassPass offers up user feedback surveys once the user logs in again after their class. Capturing this information at a moment of high-interest helps to more accurately rank the difficulty of the classes. Doing this helps ClassPass offer the right level of class to its users.
Bad Product Design: Netflix’s Autoplay Feature

It sounds like a no-brainer. If someone is hovering their mouse over a movie or a TV show, they’re clearly interested in it and you should show them more. So when you pause over a new movie, whose cover image has caught your attention, Netflix will show you a looped trailer or preview.
So why is this considered bad design?
Since the MySpace days, UX designers have known that autoplaying audio is very off-putting and disorienting for users. The way Netflix has implemented the feature, also means that key information like the title and genre disappears. Many users report having to delicately navigate the website and keep their cursor in the margins to avoid the interruption to their browsing. Twitter is rife with jokes about how annoying the feature is.
Moral of the story? Don’t autoplay audio!
Good Product Design: The Rest of Netflix
It’s pretty hard to criticize Netflix when it comes to UX design since it’s generally accepted to be a benchmark of excellent design.
One of the design features which is most notably responsible for its success is the endless A/B testing of the interface. Netflix consistently tests not only the content to show to users (will they click on a comedy or a tragedy) but also the cover art of their content (will they click on Thor, Black Widow, or Iron Man to watch The Avengers?).
Personalization is a great asset to any product’s toolkit. It helps the user to feel like the product was made for them. Once they’ve curated their own list of content, the product feels like theirs and reduces your risk of losing them.
Jobs in Product Design
Like job titles in the product world, product design jobs are not so easy to define. It’s important to remember that each company handles product design slightly differently, and job titles may vary.
Product Manager vs Product Designer
When we look at the Product Designer job description, we might see a lot of overlap with the PM role, depending on the company. Generally, a Product Manager owns more of the product vision. They define the problem, have a deep understanding of their users, work with stakeholders, and own the roadmap.
A Product Designer has more of an artistic flair. They take the problem defined by the PM, and create research-driven design concepts which will solve the problem. They collaborate with engineers to ensure that what’s being built matches the criteria of the UX honeycomb.
Meet the Team
UX Designer: They may also be called Interaction Designer, Information Architect, Experience Designers. Wireframes are their bread and butter. They’re focused on information hierarchy, flows, interactivity, and they’re helping you map that out.
Visual Designer: A Visual Designer helps your product design team make your product look like yours, and nobody else’s. With so many digital designs taking a clean, minimalist look, it’s very easy to accidentally (or not) design a carbon copy of your competitor…just with your logo. That’s not what you want! Your visual designer works with the aesthetics of your product.
Content Partner: Admittedly, Content Partners can be difficult to fit into the budget! But words matter, and you need a Copywriter to make sure the language of your product sounds natural. This is especially important for global products. Companies like Spotify, Google, and Apple, all need people who can translate and create content for each territory.
Researcher: The people who tell you the what, why, and how to make sure your product is successful. Good design has to be data-driven. Your researchers will be able to tell you what works, what people like, and what users respond to. Using that information to collaborate with the rest of the product team will lead to some winning product design!
Product Design Leaders to Follow in 2020
Don’t take our word for it – learn from the best! Here are some of the top product design leaders you need to follow:
Julie Zhuo: Julie spent 11 years as VP of Product Design at Facebook, and states her career highlight is “helping Facebook scale from 8 million college students to billions of users worldwide.” She’s also the bestselling author of The Making of a Manager.
Abigail Hart Gray: Abigail is a Director of UX at Google. Before she moved to Google she had a lucrative career, taking on roles as leading UX Manager in several companies. The most recent was her position as the Head of Design at Northwestern Mutual. There she was in charge of all UX and product design. She succeeded in facilitating the incredible growth of the company and introducing a new mentality towards design.
Pablo Stanley: Pablo has an impressive resume, including Design Lead at InVision, Staff Designer at Lyft, and Co-Founder of Blush. Well known for his entertaining talks, he’s always sharing resources and inspiration for those looking to learn more about design and be inspired.
Uyen Vicky Vo: A rising start in UX thought leadership, Vicky is an award-winning UX designer, currently with Doordash. This is the person to follow if you want to keep up-to-date on the hottest UX trends, and what the future will bring for product design.
Design for Product Managers

As a Product Manager, you’ll be working very closely with product designers, and the design of your product must absolutely be at the forefront of your mind.
Does this mean you need to be able to design a user interface, or create user flows, or pick out the perfect color scheme? No.
When we asked Innovatemap’s Principal Product Partner, Anna Eaglin, how Product Managers can form a strong relationship with designers, she said; “tell them the what, not the how.” You can give your product design team all the information and tools they need to complete a task, but don’t tell them how to do it.
Ask for feedback and create a collaborative atmosphere. If your design team feels like you’re open to hearing their opinions, you’ll be more informed and more likely to make the best product design decisions.
Although you don’t have to be a designer to be a Product Manager you can bring in design thinking. You’re the person guiding the development of your product, and you’re the person who can make design a priority.
Here are some resources to get you started:
Invision’s Design Maturity Model: A great report on the value of bringing design thinking into your business.
Don’t Make Me Think by Steve Krug: Not just a product design book, and loved by all manner of digital professionals.
About Face: A great product design book that focuses on the essentials of interaction design.
UX Collective: A repository of articles on UX design from a variety of perspectives.
Product Design Interview Questions
For a company that is heavily invested in design thinking, you might be asked some product design interview questions. Even for a Product Manager role!
You won’t be asked to create a prototype on the spot, but you should prepare some answers to question like:
How should a good design process start?
What comes first, product, or style?
Tell us about a time when you simplified a complex situation or problem. What made you seek out a simpler approach?
You start working on a new desktop/mobile/web app. What are your first steps?
How do you keep up with the latest design trends?
Have some thoughts on Product Design? Or do you have lots of questions? Join our communities for product people on Slack, or Facebook.



